Telemonitoring: 3 opportunities for cardiology practice teams
More expertise, more structure & less stress: with SaniQ HERZ, MFAs benefit from more relaxed patients, predictable processes and new digital skills.
More expertise, more structure & less stress: with SaniQ HERZ, MFAs benefit from more relaxed patients, predictable processes and new digital skills.

1. more stable patients - more relaxed daily practice routine
Telemonitoring with SaniQ HERZ reduces the risk of decompensation and hospitalisation for patients. Thanks to continuous monitoring, they feel safer and better informed. MFAs who use SaniQ HERZ report more relaxed patients and a more pleasant dialogue atmosphere.
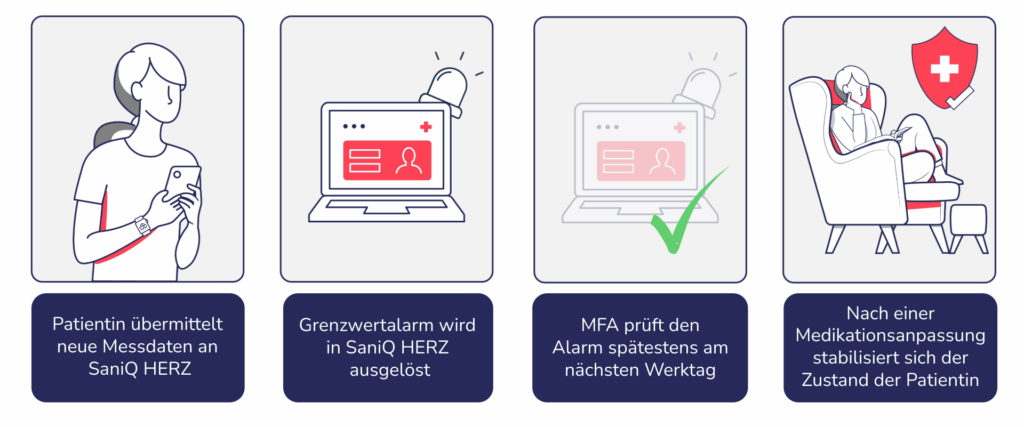
Proactive & efficient: How to prevent decompensation with SaniQ HERZ
2. structured processes - more predictability
Stable patients reduce the amount of care required by the practice team. They are less likely to spontaneously report to the practice between appointments. Thanks to the early warning system, you can recognise risks at an early stage and act efficiently before the patient arrives at the practice with severe symptoms. The daily tasks in SaniQ HERZ can also be processed flexibly and in a structured manner, which makes everyday practice life more predictable and structured overall.
3. digital competences in a future field of medicine
With SaniQ HERZ, MFAs acquire sought-after skills in digital medicine: daily use of the platform and our advanced training as a digital practice manager will make you an expert in cardiological telemonitoring. You will deepen your medical understanding and actively shape modern care that significantly improves patients' quality of life.
Certified further training for MFAs
SaniQ HERZ Specialist
Become a pioneer in digital cardiac medicine and book your training to become a SaniQ HEART Specialist now
Practical implementation with SaniQ HERZ
The introduction of telemonitoring requires a structured approach. A step-by-step approach, starting with a small group of suitable patients, has proved successful. The technical familiarisation is straightforward and our support team will accompany you during the implementation phase.
Most practices report a familiarisation period of around four to six weeks, after which the benefits of the system become clear: more structured workflows, more satisfied patients and enhanced specialist skills in a pioneering area of medicine.
These articles might be of interest to you:

SaniQ HERZ Praxis des Jahres 2025
Inmitten des ländlichen Rheinland-Pfalz hat Dr. Naim Abujarour das Telemonitoring bei Herzinsuffizienz erfolgreich etabliert. Dafür wurde seine kardiolgische Praxis jetzt als „SaniQ Praxis des Jahres“ ausgezeichnet.

Bleiben Sie rund um SaniQ HERZ auf dem Laufenden und abonnieren Sie unseren Newsletter!

