Heart failure case study: telemonitoring prevents cardiac decompensation
Heart failure case study: telemonitoring prevents cardiac decompensation
A concrete case from a cardiological group practice in Krefeld shows how telemonitoring of important vital signs and direct communication with patients can help to identify and treat critical events at an early stage.

Patient background
Patient
Age: 67 years
Illness: Heart failure
Practice: Internal medicine and cardiology group practice, Krefeld
Medical history
The patient was referred to specialist cardiological treatment by the HA in November 2022 with an anterior wall infarction. He had already been hospitalised several times due to cardiac decompensations.
Comorbidities:
- Three-vessel coronary artery disease with moderate reduced LV function
- arterial hypertension
- Hypercholesterolaemia
- COPD with emphysema
- chronic renal failure
- ischaemic cardiomyopathy
- Sleep apnoea
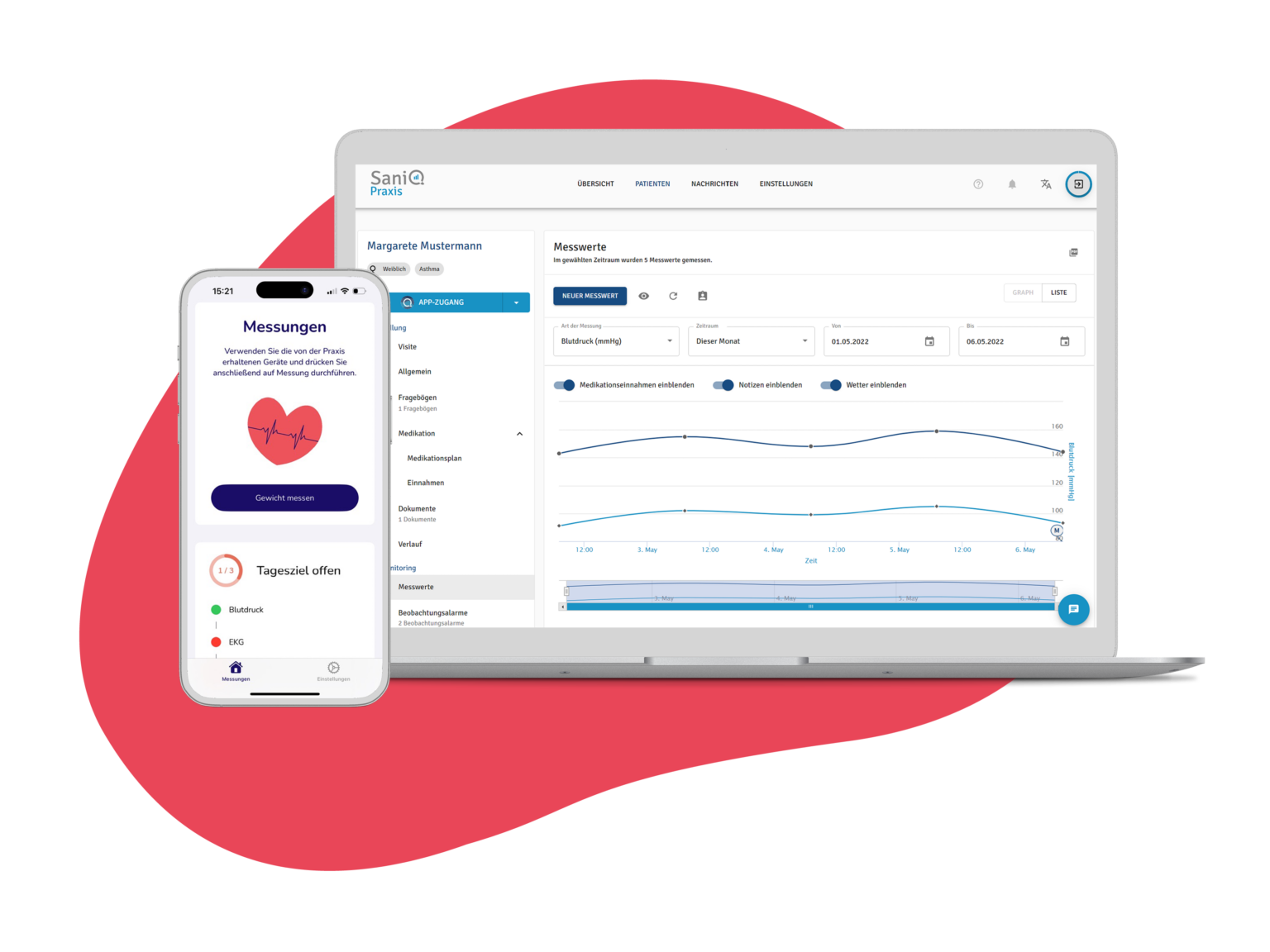
Telemonitoring
Start telemonitoring: Spring 2023
Software: SaniQ
Observed vital signs:
- Blood pressure
- Body weight
- ECG
Event history
Critical event
The patient transmits a sudden weight gain via the SaniQ app.
Limit value exceeded
Exceeding the limit value triggers a monitoring alarm in SaniQ.
The patient also reports water retention in both feet via the chat function.

Intervention
The treating doctor prescribes an increased dose of torasemide (10 mg) for 5 days in the medication schedule for drainage.

Result
The administration of the medication takes effect quickly: on 14 April, the patient reports a normalised body weight.
The threat of cardiac decompensation could be averted at an early stage by adjusting the medication.

In our practice, cardiac decompensations have already been prevented in several cases by telemonitoring without the need for a visit to the practice. Of course, our patients think this is great and it saves us an immense amount of time in our practice!
Ms Schäffer, MFA and telemonitoring specialist in the internal medicine-cardiology group practice, Krefeld

3 steps to telemonitoring
Telemonitoring offers many advantages for cardiologists and patients. With the SaniQ platform, both can quickly get started with telemonitoring.
These articles might be of interest to you:

Cardiac telemonitoring for heart failure
Cardiology practices have been able to bill for cardiac telemonitoring in heart failure since 2022. We will show you how you can meet the requirements and offer your patients modern care.

